Home care and home health care are two distinct types of services designed to support individuals in their homes, but they differ in the nature and scope of care provided.
Home Care
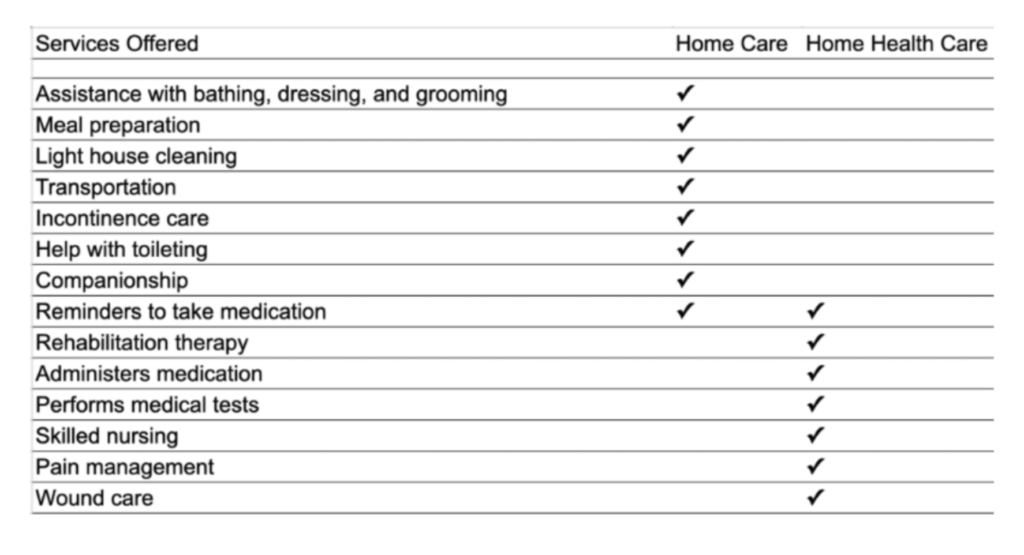
Home care refers to non-medical services that help individuals with daily living activities. These services are typically provided by caregivers or aides and focus on improving the quality of life and ensuring the person’s well-being and safety at home. Home care can include:
- Personal care (e.g., bathing, dressing, grooming)
- Assistance with mobility (e.g., transferring from bed to chair)
- Help with household tasks (e.g., cleaning, laundry, meal preparation)
- Companionship and social interaction
- Assistance with shopping and errands
- Help with medication reminders (but not administration)
Home care is often sought for elderly individuals, people with disabilities, or those recovering from an illness or surgery who do not need medical care but require help with daily activities.
Home Health Care
Home health care, on the other hand, involves medical services provided in the home by licensed healthcare professionals such as nurses, therapists, and home health aides. This type of care is typically prescribed by a physician and is aimed at treating illnesses or injuries. Home health care can include:
- Skilled nursing care (e.g., wound care, injections, monitoring vital signs)
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech therapy
- Administration and management of medications
- Medical tests (e.g., blood tests)
- Education for the patient and family on disease management
- Assistance with medical equipment and supplies
Home health care is often used for individuals who are recovering from surgery, managing chronic conditions, or requiring ongoing medical attention and supervision.
Key Differences
- Nature of Services:
- Home Care: Non-medical support and assistance with daily living activities.
- Home Health Care: Medical services and treatments provided by healthcare professionals.
2. Providers:
- Home Care: Caregivers or aides without medical training.
- Home Health Care: Licensed nurses, therapists, and other medical professionals.
3. Focus:
- Home Care: Enhancing quality of life, safety, and independence.
- Home Health Care: Treating medical conditions and managing health.
4. Payment and Insurance:
- Home Care: Typically, not covered by insurance; paid out-of-pocket or through long-term care insurance.
- Home Health Care: Often covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance plans when medically necessary and prescribed by a physician.
Understanding these differences can help individuals and families choose the right type of care based on their specific needs and circumstances.